Table of Contents
Cosmos’ ATOM staking refers to the act of locking up ATOMs for a period of time in order to provide economic security for the blockchain. Cosmos’ ecosystem is made up of hubs and Zones (application-specific blockchains). The Zones are connected to hubs, which, in turn, are connected to other hubs, creating a so-called “Internet of Blockchains.” Here, anyone can develop Hub or Zone, as well as accept or refuse to connect with other blockchains. Cosmos’ main chain is Cosmos Hub, whose primary token is the ATOM.
Key Takeaways
- Founded in 2014, Cosmos has the goal of becoming the “Internet of Blockchains.”
- Its main chain is the Cosmos Hub, with its primary cryptocurrency ATOM
- The ATOM can be used to pay transaction fees, vote on platform decisions, and staked by delegating it to a validator
- Staking entails locking up an amount of ATOM for some time, and only the unstaked amount can be used in the meantime.
- ATOM’s main risk is connected to the validator due to “slashing,” which is why trust is an important factor.
The Cosmos Blockchain
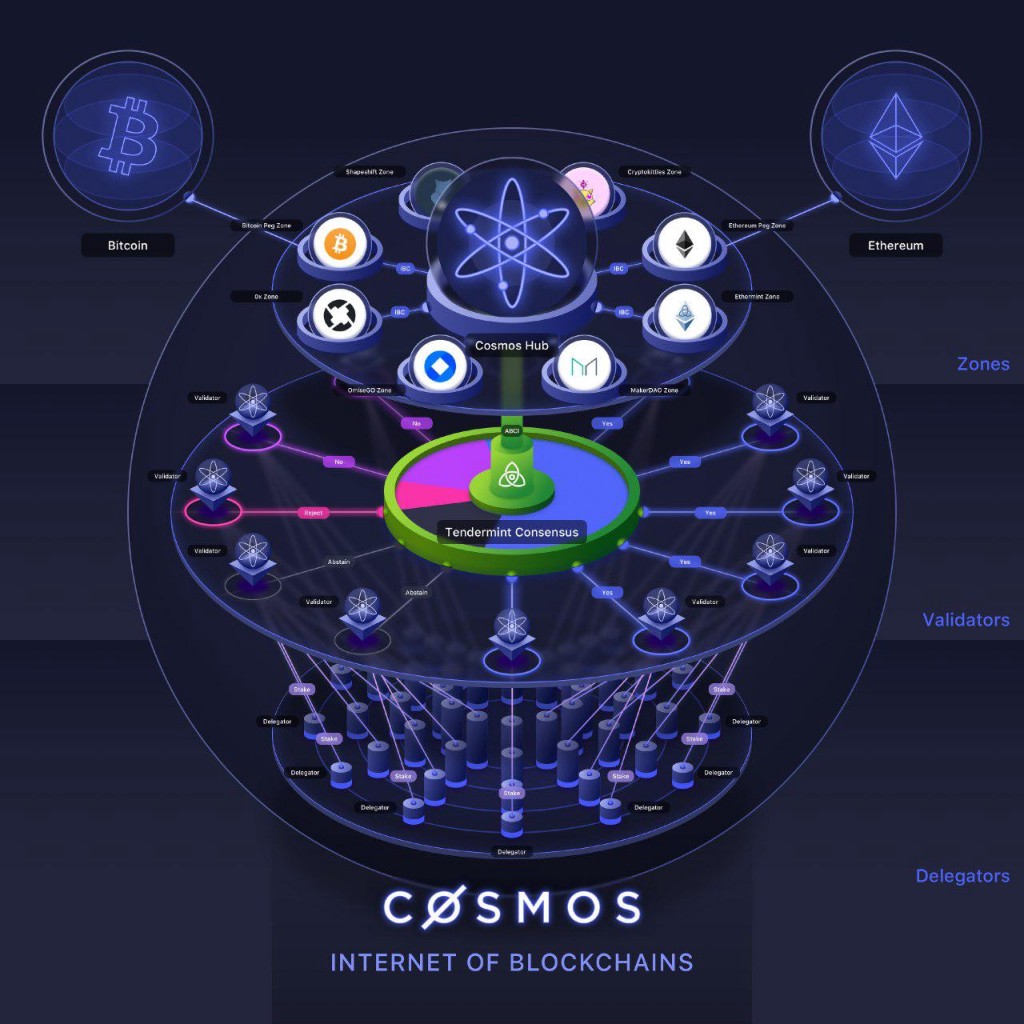
Cosmos, a project aimed at establishing an interoperable network of diverse blockchains, was founded by Jae Kwon and Ethan Buchman in 2014. It describes itself as a blockchain 3.0 since it builds on top of what Bitcoin and Ethereum have set. Its goal is to create a so-called “Internet of Blockchains,” a decentralized network of blockchains that can communicate with each other. Using Cosmos enables blockchains to preserve their sovereignty, execute transactions rapidly, and connect with other blockchains in the ecosystem, which makes it ideal for a wide range of uses. To bring their vision to life, the chain uses Tendermint, the Cosmos SDK, IBC, and other open-source tools to allow others to swiftly create scalable, custom, secure, and interoperable blockchain apps.
What is the ATOM?

As mentioned above, ATOM is the primary cryptocurrency of the Cosmos Hub, and by Cosmos crypto staking, stakers are contributing to the Hub’s security and governance. The coin has three main functions:
- Users use it to pay transaction fees that are proportionate to the amount of computational power needed.
- It allows its holders to vote on on-chain governance propositions and help shape the future of the Cosmos Hub. The higher the amount of ATOM, the more voting power one has in platform decisions.
- And, of course, the coin can be staked behind a validator to gain rewards by participating in the consensus algorithm. Users can earn more ATOMs using the Proof of Stake system by delegating their ATOM to one or more of the Cosmos Hub blockchain’s top 125 validators.
ATOM is an inflationary currency that was distributed through an Initial Coin Offering and has no supply limit. This is possible thanks to Tendermint Core, which enables stakers to receive newly minted ATOM. Based on the staked amount and the number of stakers, the inflation rate changes in real-time.
How Does Cosmos ATOM Staking Work and How to Stake ATOM?
Now as a beginner you might ask yourself, “is staking cosmos worth it?”. To answer that, let’s see how staking Cosmos works and how to kick off Cosmos coin staking.
By staking Cosmos, stakers actually delegate an amount of their ATOM to a validator, themselves becoming delegators. After staking, they choose how much of their ATOM they want to delegate. Since staking entails locking up a certain amount of the cryptocurrency, during this time, only the unstaked amount can be used to perform transactions. The validators’ responsibilities include validating and approving transactions on the blockchain.
The higher the amount of ATOM delegated to them, the more transactions they can validate, making them more powerful. In this sense, delegation is basically a vote that signals a delegator’s trust in their chosen validator. The higher the number of validated transactions, the more money they can gain.
These rewards are then distributed to the delegators, which is how they earn interest. Users can also unstake their ATOMs, during which any unclaimed rewards will be automatically claimed. After choosing the amount to unstake, it will become “unbonding” and can only be used after 21 days. Rewards will also not be gained with this unstaked ATOM within this period.
Benefits of Staking Cosmos
Similar to other cryptocurrencies, users can earn passive income by staking their ATOMs; otherwise, the ATOM they hold will get diluted with time. Another benefit is that the transaction fees are also paid to the coin holders. Besides that, having a large amount of cryptocurrency means the chances of being selected as a validator are higher. And if chosen, they can verify new blocks on the Cosmos blockchain. Lastly, unlike mining equipment, staked cryptocurrencies do not lose value over time.
Is ATOM Staking Safe?
However, cosmos ATOM staking cannot be considered completely safe. If a validator misbehaves, the ATOM that was delegated to them can be subject to partial “slashing” (the ATOMs are forfeited and will not be recovered). There are two types of slashing that can happen on the Cosmos Hub:
Slashing by 0.01%
Being offline for too long can result in this type of slashing. Validators are required to sign a minimum of 500 out of the last 10,000 blocks for uptime to be achieved. Otherwise, a downtime slash will occur.
Slashing by 5%
This type can occur if a validator double-signs (signing two different blocks at the same height). Compared to the previous, such slashing is much more difficult to predict, as it can result not only from inappropriate operation practices but also due to the validator operator’s malicious intent. As with any delegation, trust between the operator and the delegator is essential. In addition, ATOM holders are advised to delegate to multiple validators in order to minimize such staking risks.
What Are Cosmos Staking Rewards and How Often Does Cosmos Pay Staking Rewards?
Cosmos staking rewards will begin to be generated soon as the staking transaction is completed. Stakeholders can use a wallet to send a transaction at any time to claim their amassed cosmos staking rewards. The rewards are produced and shared with the stakeholders through two methods:
Transaction Fees
Staked ATOM holders receive a share of transaction fees earned on the Cosmos Hub.
Newly Created ATOM
To reward stakers, the total supply of ATOM is inflated. Since there are people who hold ATOMs but do not stake, they do not receive the rewards, and their ATOMs get diluted with time.
Dictionary
Hub – a blockchain whose main function is to support the routing of messages between Zones and ensure a constant state for blockchains it’s connected to.
Zone – an independent blockchain that an application developer uses as an application-specific blockchain.
Tendermint Core – a blockchain application platform that acts as a database, web server, and supporting libraries.
Tendermint – allows developers to create blockchains without the need to make things from scratch.
Cosmos SDK – a modular development framework that enables developers to create Zones with ease.
IBC (Inter-Blockchain Communication) – a protocol that allows value and data to be exchanged in a decentralized way between fast-finality blockchains.
Final Thoughts
To conclude, ATOM is the main cryptocurrency of the Cosmos blockchain. It can be used in a variety of ways, including voting on blockchain proposals and staking. By staking ATOM, users delegate a certain amount of ATOM to a validator, who will validate and approve transactions on the blockchain. The disadvantage of staking Cosmos’ ATOM is that if the validator misbehaves, the delegated ATOM can be partially “slashed.” However, such a risk can be minimized by delegating to several validators.
Disclaimer: The opinion expressed here is not investment advice – it is provided for informational purposes only. It does not necessarily reflect the opinion of EGG Finance. Every investment and all trading involves risk, so you should always perform your own research prior to making decisions. We do not recommend investing money you cannot afford to lose.
 English
English Français
Français Español
Español Bahasa Indonesia
Bahasa Indonesia 中文 (中国)
中文 (中国) Русский
Русский Português
Português Deutsch
Deutsch

